🚀 Able to supercharge your AI workflow? Attempt ElevenLabs for AI voice and speech technology!
On this article, you’ll study three dependable methods — ordinal encoding, one-hot encoding, and goal (imply) encoding — for turning categorical options into model-ready numbers whereas preserving their which means.
Subjects we’ll cowl embody:
- When and tips on how to apply ordinal (label-style) encoding for really ordered classes.
- Utilizing one-hot encoding safely for nominal options and understanding its trade-offs.
- Making use of goal (imply) encoding for high-cardinality options with out leaking the goal.
Time to get to work.
3 Sensible Methods to Encode Categorical Options for Machine Studying
Picture by Editor
Introduction
In case you spend any time working with real-world information, you shortly understand that not every part is available in neat, clear numbers. In truth, many of the attention-grabbing facets, the issues that outline folks, locations, and merchandise, are captured by classes. Take into consideration a typical buyer dataset: you’ve received fields like Metropolis, Product Kind, Training Stage, and even Favourite Coloration. These are all examples of categorical options, that are variables that may tackle certainly one of a restricted, fastened variety of values.
The issue? Whereas our human brains seamlessly course of the distinction between “Pink” and “Blue” or “New York” and “London,” the machine studying fashions we use to make predictions can’t. Fashions like linear regression, resolution bushes, or neural networks are basically mathematical capabilities. They function by multiplying, including, and evaluating numbers. They should calculate distances, slopes, and chances. Once you feed a mannequin the phrase “Advertising,” it doesn’t see a job title; it simply sees a string of textual content that has no numerical worth it could use in its equations. This incapacity to course of textual content is why your mannequin will crash immediately should you attempt to prepare it on uncooked, non-numeric labels.
The first objective of function engineering, and particularly encoding, is to behave as a translator. Our job is to transform these qualitative labels into quantitative, numerical options with out shedding the underlying which means or relationships. If we do it proper, the numbers we create will carry the predictive energy of the unique classes. As an illustration, encoding should make sure that the quantity representing a high-level Training Stage is quantitatively “increased” than the quantity representing a decrease stage, or that the numbers representing totally different Cities replicate their distinction in buy habits.
To sort out this problem, we now have advanced sensible methods to carry out this translation. We’ll begin with probably the most intuitive strategies, the place we merely assign numbers primarily based on rank or create separate binary flags for every class. Then, we’ll transfer on to a robust approach that makes use of the goal variable itself to construct a single, dense function that captures a class’s true predictive affect. By understanding this development, you’ll be outfitted to decide on the proper encoding methodology for any categorical information you encounter.
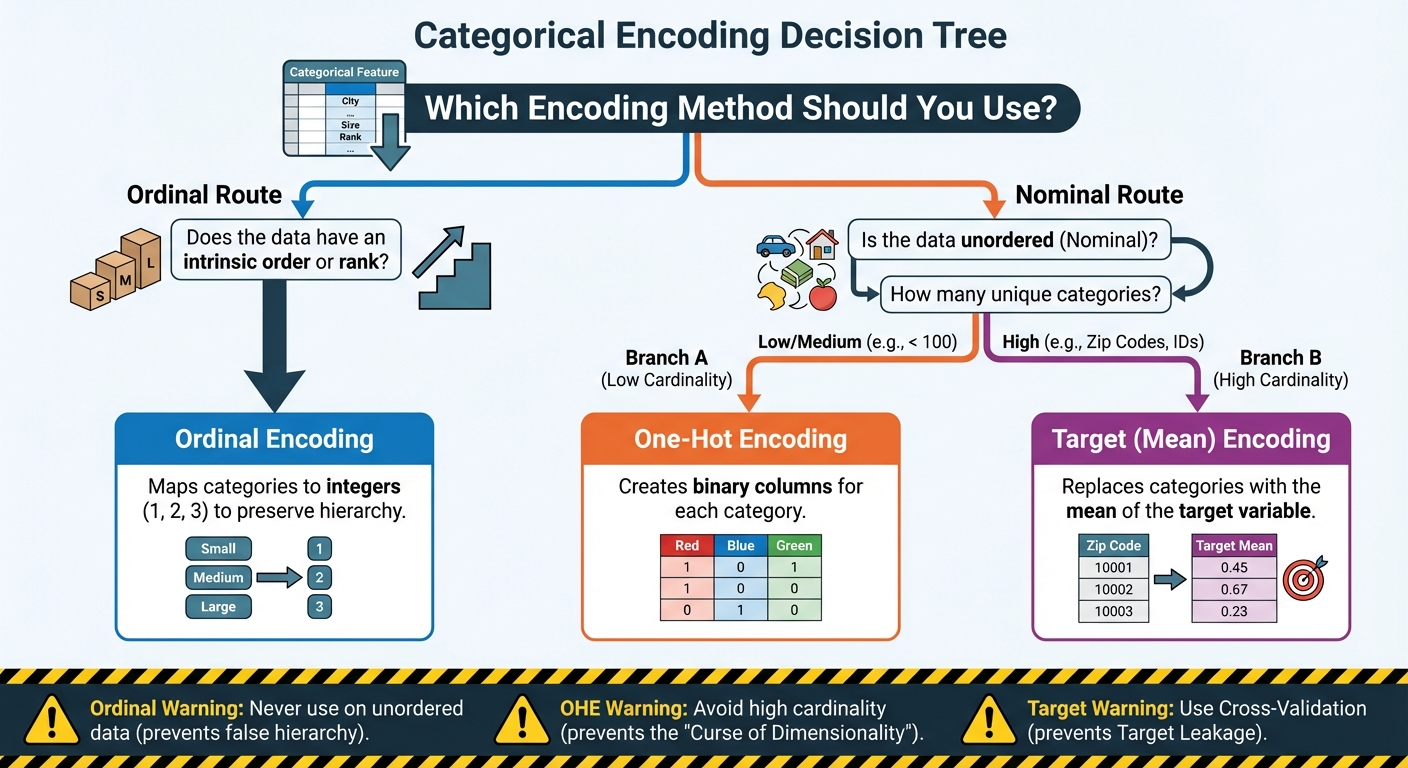
3 Sensible Methods to Encode Categorical Options for Machine Studying: A Flowchart (click on to enlarge)
Picture by Editor
1. Preserving Order: Ordinal and Label Encoding
The primary, and easiest, translation approach is designed for categorical information that isn’t only a assortment of random names, however a set of labels with an intrinsic rank or order. That is the important thing perception. Not all classes are equal; some are inherently “increased” or “extra” than others.
The most typical examples are options that characterize some type of scale or hierarchy:
- Training Stage: (Excessive College => Faculty => Grasp’s => PhD)
- Buyer Satisfaction: (Very Poor => Poor => Impartial => Good => Glorious)
- T-shirt Measurement: (Small => Medium => Giant)
Once you encounter information like this, the simplest option to encode it’s to make use of Ordinal Encoding (usually informally known as “label encoding” when mapping classes to integers).
The Mechanism
The method is simple: you map the classes to integers primarily based on their place within the hierarchy. You don’t simply assign numbers randomly; you explicitly outline the order.
For instance, if in case you have T-shirt sizes, the mapping would appear to be this:
| Unique Class | Assigned Numerical Worth |
|---|---|
| Small (S) | 1 |
| Medium (M) | 2 |
| Giant (L) | 3 |
| Additional-Giant (XL) | 4 |
By doing this, you’re instructing the machine that an XL (4) is numerically “extra” than an S (1), which appropriately displays the real-world relationship. The distinction between an M (2) and an L (3) is mathematically the identical because the distinction between an L (3) and an XL (4), a unit improve in measurement. This ensuing single column of numbers is what you feed into your mannequin.
Introducing a False Hierarchy
Whereas Ordinal Encoding is the proper selection for ordered information, it carries a significant danger when misapplied. You should by no means apply it to nominal (non-ordered) information.
Take into account encoding an inventory of colours: Pink, Blue, Inexperienced. In case you arbitrarily assign them: Pink = 1, Blue = 2, Inexperienced = 3, your machine studying mannequin will interpret this as a hierarchy. It should conclude that “Inexperienced” is twice as giant or essential as “Pink,” and that the distinction between “Blue” and “Inexperienced” is similar because the distinction between “Pink” and “Blue.” That is virtually definitely false and can severely mislead your mannequin, forcing it to study non-existent numerical relationships.
The rule right here is easy and agency: use Ordinal Encoding solely when there’s a clear, defensible rank or sequence between the classes. If the classes are simply names with none intrinsic order (like varieties of fruit or cities), you need to use a distinct encoding approach.
Implementation and Code Rationalization
We are able to implement this utilizing the OrdinalEncoder from scikit-learn. The bottom line is that we should explicitly outline the order of the classes ourselves.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
from sklearn.preprocessing import OrdinalEncoder import numpy as np
# Pattern information representing buyer training ranges information = np.array([[‘High School’], [‘Bachelor’s’], [‘Master’s’], [‘Bachelor’s’], [‘PhD’]])
# Outline the specific order for the encoder # This ensures that ‘Bachelor’s’ is appropriately ranked under ‘Grasp’s’ education_order = [ [‘High School’, ‘Bachelor’s’, ‘Master’s’, ‘PhD’] ]
# Initialize the encoder and cross the outlined order encoder = OrdinalEncoder(classes=education_order)
# Match and remodel the information encoded_data = encoder.fit_transform(information)
print(“Unique Information:n”, information.flatten()) print(“nEncoded Information:n”, encoded_data.flatten()) |
Within the code above, the essential half is setting the classes parameter when initializing OrdinalEncoder. By passing the precise record education_order, we inform the encoder that ‘Excessive College’ comes first, then ‘Bachelor’s’, and so forth. The encoder then assigns the corresponding integers (0, 1, 2, 3) primarily based on this practice sequence. If we had skipped this step, the encoder might need assigned the integers primarily based on alphabetical order, which might destroy the significant hierarchy we needed to protect.
2. Eliminating Rank: One-Sizzling Encoding (OHE)
As we mentioned, Ordinal Encoding solely works in case your classes have a transparent rank. However what about options which are purely nominal, which means they’ve names, however no inherent order? Take into consideration issues like Nation, Favourite Animal, or Gender. Is “France” higher than “Japan”? Is “Canine” mathematically higher than “Cat”? Completely not.
For these non-ordered options, we want a option to encode them numerically with out introducing a false sense of hierarchy. The answer is One-Sizzling Encoding (OHE), which is by far probably the most extensively used and most secure encoding approach for nominal information.
The Mechanism
The core thought behind OHE is easy: as a substitute of changing a single class column with a single quantity, it’s changed with a number of binary columns. For each distinctive class in your authentic function, you create a brand-new column. These new columns are sometimes known as dummy variables.
For instance, in case your authentic Coloration function has three distinctive classes (Pink, Blue, Inexperienced), OHE will create three new columns: Color_Red, Color_Blue, and Color_Green.
In any given row, solely a kind of columns will probably be “sizzling” (a price of 1), and the remaining will probably be 0.
| Unique Coloration | Color_Red | Color_Blue | Color_Green |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pink | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Blue | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Inexperienced | 0 | 0 | 1 |
This methodology is sensible as a result of it fully solves the hierarchy drawback. The mannequin now treats every class as a totally separate, unbiased function. “Blue” is now not numerically associated to “Pink”; it simply exists in its personal binary column. That is the most secure and most dependable default selection when you already know your classes don’t have any order.
The Commerce-off
Whereas OHE is the usual for options with low to medium cardinality (i.e., a small to reasonable variety of distinctive values, sometimes below 100), it shortly turns into an issue when coping with high-cardinality options.
Cardinality refers back to the variety of distinctive classes in a function. Take into account a function like Zip Code in america, which may simply have over 40,000 distinctive values. Making use of OHE would power you to create 40,000 brand-new binary columns. This results in two main points:
- Dimensionality: You instantly balloon the width of your dataset, creating an enormous, sparse matrix (a matrix containing largely zeros). This dramatically slows down the coaching course of for many algorithms.
- Overfitting: Many classes will solely seem a couple of times in your dataset. The mannequin may assign an excessive weight to certainly one of these uncommon, particular columns, primarily memorizing its one look reasonably than studying a basic sample.
When a function has hundreds of distinctive classes, OHE is solely impractical. This limitation forces us to look past OHE and leads us on to our third, extra superior approach for coping with information at an enormous scale.
Implementation and Code Rationalization
In Python, the OneHotEncoder from scikit-learn or the get_dummies() perform from pandas are the usual instruments. The pandas methodology is usually simpler for fast transformation:
|
import pandas as pd
# Pattern information with a nominal function: Coloration information = pd.DataFrame({ ‘ID’: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5], ‘Coloration’: [‘Red’, ‘Blue’, ‘Red’, ‘Green’, ‘Blue’] })
# 1. Apply One-Sizzling Encoding utilizing pandas get_dummies df_encoded = pd.get_dummies(information, columns=[‘Color’], prefix=‘Is’)
print(df_encoded) |
On this code, we cross our DataFrame information and specify the column we wish to remodel (Coloration). The prefix='Is' merely provides a clear prefix (like ‘Is_Red‘) to the brand new columns for higher readability. The output DataFrame retains the ID column and replaces the only Coloration column with three new, unbiased binary options: Is_Red, Is_Blue, and Is_Green. A row that was initially ‘Pink’ now has a 1 within the Is_Red column and a 0 within the others, reaching the specified numerical separation with out imposing rank.
3. Harnessing Predictive Energy: Goal (Imply) Encoding
As we established, One-Sizzling Encoding fails spectacularly when a function has excessive cardinality, hundreds of distinctive values like Product ID, Zip Code, or Electronic mail Area. Creating hundreds of sparse columns is computationally inefficient and results in overfitting. We’d like a method that may compress these hundreds of classes right into a single, dense column with out shedding their predictive sign.
The reply lies in Goal Encoding, additionally incessantly known as Imply Encoding. As an alternative of relying solely on the function itself, this methodology strategically makes use of the goal variable (Y) to find out the numerical worth of every class.
The Idea and Mechanism
The core thought is to encode every class with the typical worth of the goal variable for all information factors belonging to that class.
As an illustration, think about you are attempting to foretell if a transaction is fraudulent (Y=1 for fraud, Y=0 for professional). In case your categorical function is Metropolis:
- You group all transactions by Metropolis
- For every metropolis, you calculate the imply of the Y variable (the typical fraud fee)
- The town of “Miami” might need a median fraud fee of 0.10 (or 10%), and “Boston” might need 0.02 (2%)
- You change the explicit label “Miami” in each row with the quantity 0.10, and “Boston” with 0.02
The result’s a single, dense numerical column that instantly embeds the predictive energy of that class. The mannequin immediately is aware of that rows encoded with 0.10 are ten occasions extra prone to be fraudulent than rows encoded with 0.01. This drastically reduces dimensionality whereas maximizing data density.
The Benefit and The Essential Hazard
The benefit of Goal Encoding is evident: it solves the high-cardinality drawback by changing hundreds of sparse columns with only one dense, highly effective function.
Nonetheless, this methodology is usually known as “probably the most harmful encoding approach” as a result of this can be very weak to Goal Leakage.
Goal leakage happens once you inadvertently embody data in your coaching information that will not be accessible at prediction time, resulting in artificially good (and ineffective) mannequin efficiency.
The Deadly Mistake: In case you calculate the typical fraud fee for Miami utilizing all the information, together with the row you’re at the moment encoding, you’re leaking the reply. The mannequin learns an ideal correlation between the encoded function and the goal variable, primarily memorizing the coaching information as a substitute of studying generalizable patterns. When deployed on new, unseen information, the mannequin will fail spectacularly.
Stopping Leakage
To make use of Goal Encoding safely, you need to make sure that the goal worth for the row being encoded isn’t used within the calculation of its function worth. This requires superior methods:
- Cross-Validation (Ok-Fold): Probably the most sturdy method is to make use of a cross-validation scheme. You cut up your information into Ok folds. When encoding one fold (the “holdout set”), you calculate the goal imply solely utilizing the information from the opposite Ok-1 folds (the “coaching set”). This ensures the function is generated from out-of-fold information.
- Smoothing: For classes with only a few information factors, the calculated imply could be unstable. Smoothing is utilized to “shrink” the imply of uncommon classes towards the worldwide common of the goal variable, making the function extra sturdy. A typical smoothing components usually includes weighting the class imply with the worldwide imply primarily based on the pattern measurement.
Implementation and Code Rationalization
Implementing protected Goal Encoding normally requires customized capabilities or superior libraries like category_encoders, as scikit-learn’s core instruments don’t provide built-in leakage safety. The important thing precept is calculating the means exterior of the first information being encoded.
For demonstration, we’ll use a conceptual instance, specializing in the results of the calculation:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 |
import pandas as pd
# Pattern information information = pd.DataFrame({ ‘Metropolis’: [‘Miami’, ‘Boston’, ‘Miami’, ‘Boston’, ‘Boston’, ‘Miami’], # Goal (Y): 1 = Fraud, 0 = Reliable ‘Fraud_Target’: [1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0] })
# 1. Calculate the uncooked imply (for demonstration solely — that is UNSAFE leakage) # Actual-world use requires out-of-fold means for security! mean_encoding = information.groupby(‘Metropolis’)[‘Fraud_Target’].imply().reset_index() mean_encoding.columns = [‘City’, ‘City_Encoded_Value’]
# 2. Merge the encoded values again into the unique information df_encoded = information.merge(mean_encoding, on=‘Metropolis’, how=‘left’)
# Output the calculated means for illustration miami_mean = df_encoded[df_encoded[‘City’] == ‘Miami’][‘City_Encoded_Value’].iloc[0] boston_mean = df_encoded[df_encoded[‘City’] == ‘Boston’][‘City_Encoded_Value’].iloc[0]
print(f“Miami Encoded Worth: {miami_mean:.4f}”) print(f“Boston Encoded Worth: {boston_mean:.4f}”) print(“nFinal Encoded Information (Conceptual Leakage Instance):n”, df_encoded) |
On this conceptual instance, “Miami” has three data with goal values [1, 1, 0], giving a median (imply) of 0.6667. “Boston” has three data [0, 0, 0], giving a median of 0.0000. The uncooked metropolis names are changed by these float values, dramatically growing the function’s predictive energy. Once more, to make use of this in an actual undertaking, the City_Encoded_Value would should be calculated rigorously utilizing solely the subset of knowledge not being educated on, which is the place the complexity lies.
Conclusion
We’ve coated the journey of reworking uncooked, summary classes into the numerical language that machine studying fashions demand. The distinction between a mannequin that works and one which excels usually comes right down to this function engineering step.
The important thing takeaway is that no single approach is universally superior. As an alternative, the precise selection relies upon totally on the character of your information and the variety of distinctive classes you’re coping with.
To shortly summarize the three sensible approaches we’ve detailed:
- Ordinal Encoding: That is your answer when you could have an intrinsic rank or hierarchy amongst your classes. It’s environment friendly, including just one column to your dataset, however it have to be reserved solely for ordered information (like sizes or ranges of settlement) to keep away from introducing deceptive numerical relationships.
- One-Sizzling Encoding (OHE): That is the most secure default when coping with nominal information the place order doesn’t matter and the variety of classes is small to medium. It prevents the introduction of false rank, however you have to be cautious of utilizing it on options with hundreds of distinctive values, as it could balloon the dataset measurement and decelerate coaching.
- Goal (Imply) Encoding: That is the highly effective reply for high-cardinality options that will overwhelm OHE. By encoding the class with its imply relationship to the goal variable, you create a single, dense, and extremely predictive function. Nonetheless, as a result of it makes use of the goal variable, it calls for excessive warning and have to be applied utilizing cross-validation or smoothing to stop catastrophic goal leakage.
🔥 Need the very best instruments for AI advertising and marketing? Take a look at GetResponse AI-powered automation to spice up your enterprise!

